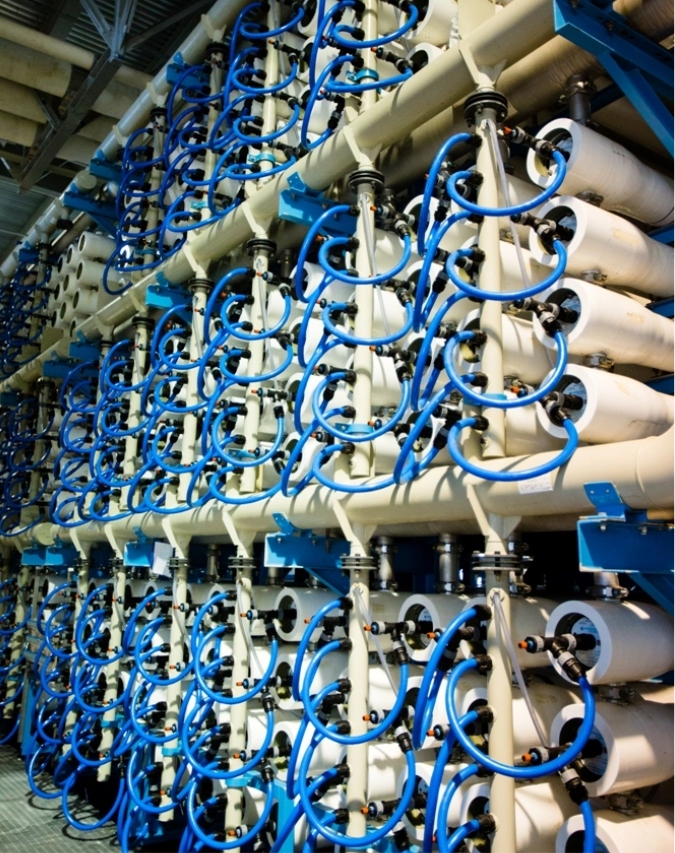
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis is a process in which a pressure greater than the natural osmotic pressure is applied on water that passes through a semipermeable membrane (RO membrane), which rejects the salts in seawater, creating a stream of fresh water and a separate stream of concentrated seawater.

RO can remove many types of molecules and ions, making it suited for potable and industrial uses. Standard osmosis involves a solvent (such as water) naturally moving from an area of low solute concentration, through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration. The movement of a pure solvent reduces the free energy of the system by equalizing solute concentrations on each side of the membrane, generating osmotic pressure.
Applying an external pressure to reverse the natural flow of solvent is called reverse osmosis. To create clean water using this process, seawater or brackish water is pressurized against one surface of the membrane, causing salt-depleted water to move across the membrane, releasing clean water from the low-pressure side.

Efficiency and increased membrane life
Reverse Osmosis membranes are subject to fouling by dissolved and suspended substances that are present in industrial effluents. Therefore, proper pretreatment is essential for the efficient, long-term operation of any membrane treatment system, as well as for better plant efficiency and increased membrane life.

IDE Water Technologies has developed two innovative technologies for treating industrial wastewater – MAXH2O Desalter and MAXH2O PFRO
IDE Water Technologies’ membrane based technologies for industrial wastewater overcome the limits of the challenging water chemistry, thus providing added value to the client by:
- Industry highest treatment recovery rates
- Minimizing effluent disposal
- Recovery of additional fresh water for reuse
- Minimizing downstream ZLD system when applicable
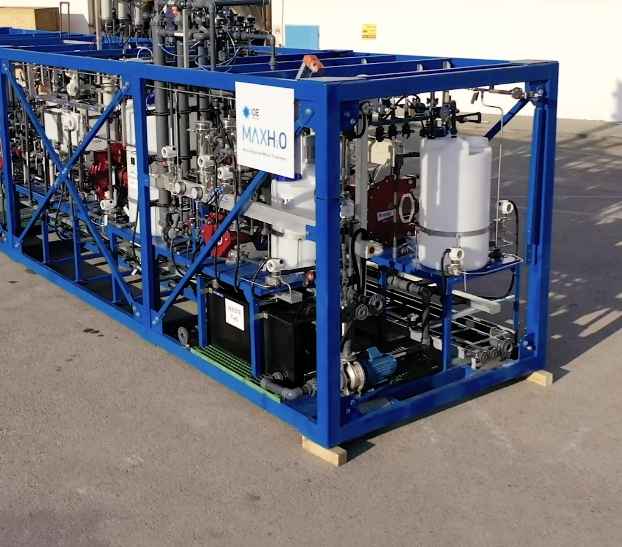




MAXH2O DESALTER SOLUTION
The MAXH2O Desalter is a state-of-the-art RO solution that includes an integrated salt precipitation cycle for high recovery applications. The MAXH2O Desalter process allows pushing the RO water treatment ability to its limit while overcoming the challenging limitation of membrane scaling and fouling – all this while achieving the industry’s highest recovery rates.
The water to be treated is recirculated through the RO system at a high shear velocity, while the sparingly soluble salts are continuously precipitated in the crystallactor, located after the membranes. The high shear velocity significantly reduces salt concentration polarization on the surface of the RO membrane. The salt precipitation unit removes sparingly soluble salts from the water, reducing the saturation of sparingly soluble salts in the recirculated brine and allowing continuous cycles through the RO system until the maximum brine osmotic pressure is reached.
The membrane remains clean and can operate up to its osmotic limit. As the precipitated crystals grow in size, they sink to the bottom of the crystallactor. Without stopping operations, the unit is periodically emptied out from the bottom and topped up with new media from above. The emptied pellets, with high solids content, are easily disposed of to landfills or other approved sites.
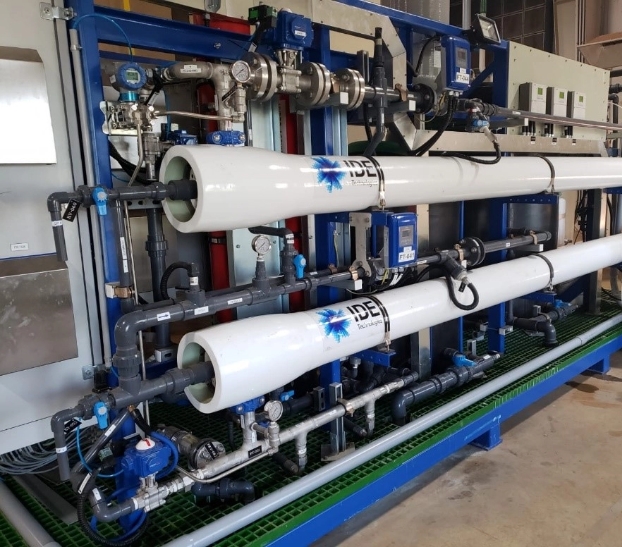




PULSE FLOW RO (PFRO)
Contrary to the standard multistage RO structure, Pulse Flow RO technology (PFRO) is a single stage process that discharges the brine flow periodically, in a pulse flow process – a small volume of brine flow is discharged at high velocity for a short time.
It is well known that salt precipitation is not immediate – it is a process over time, known as the induction time. This is the time required for the crystal to reach the size and shape at which it precipitates. The length of induction time is determined by thermodynamics and can take several minutes.
Our patented Pulse Flow RO (PFRO) technology works by discharging the brine in periodic pulses of short duration, thus not allowing sufficient time for crystal formation, i.e., for the salts to precipitate. A flow of wastewater is pushed through the RO membrane in timed pulses, after which the membrane is flushed and cleaned. This process is then repeated.
This is an innovative method for operating reverse osmosis water reuse systems that allows high recovery and high flux, at competitive operation costs.
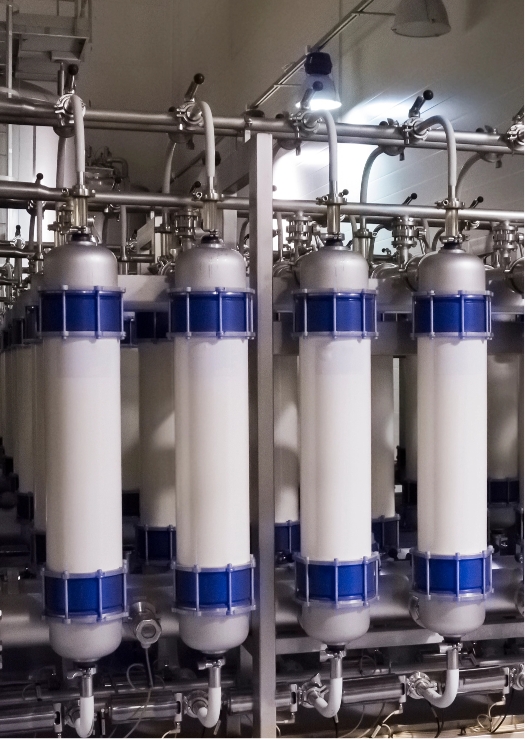




UF + NF
UF (Ultrafiltration)
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a membrane filtration process which uses hydrostatic pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane. The pore size of the ultrafiltration membrane, usually 0.01 to 0.1 micrometers (microns), creates a pressure-driven barrier to suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, endotoxins and other pathogens to produce water with very high purity and low silt density.
Nano Filtration System
Nanofiltration (NF), like RO, is a pressure-driven membrane separation process with the difference in the pore size of the NF membranes. NF membranes have larger pores, as compared to RO membranes. NF is selective in removing ions. While it can remove divalent ions (e.g., calcium, magnesium), it allows some monovalent ions (e.g., sodium) to pass through. This makes NF useful for applications where some ions are desired in the treated water. NF is often used for water softening, removal of specific ions, color, and organic matter in water treatment processes.
Related Solutions
All solutions

Contact an Expert