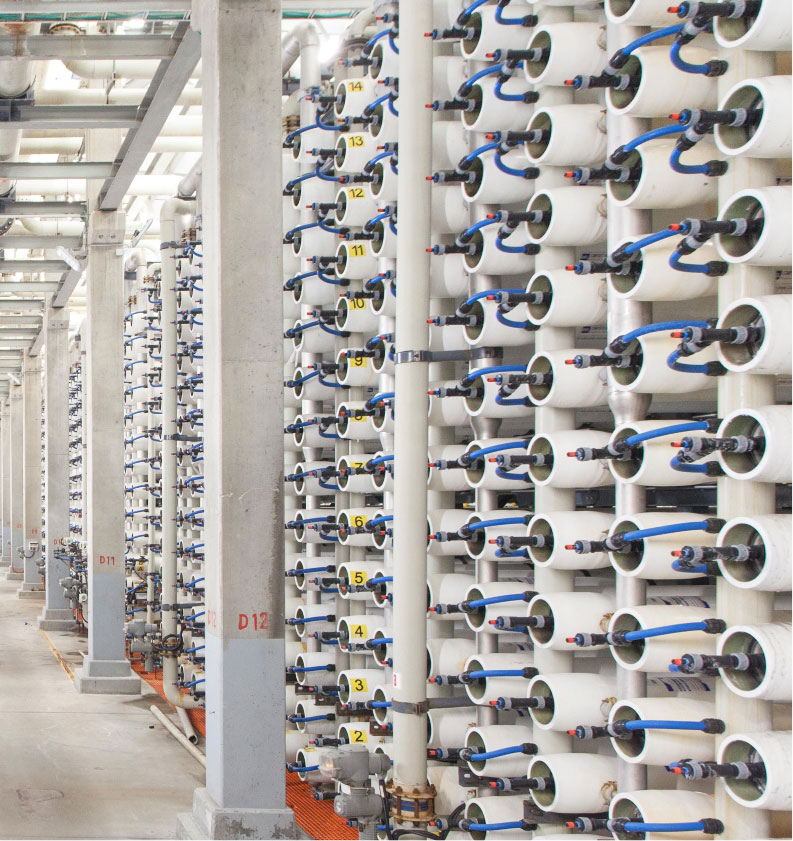
What is Seawater Desalination?
The world is in need of fresh water. Water is fundamental to life, yet sustainable freshwater resources are increasingly limited in quantity and quality. Population growth, changing water consumption patterns, and climate change threaten our freshwater supplies.
Seawater desalination is the process of removal of salts and dissolved solids from seawater. It is an important and vital solution that can combat water scarcity and an alternative, feasible and reliable source of water to ensure water sustainability.



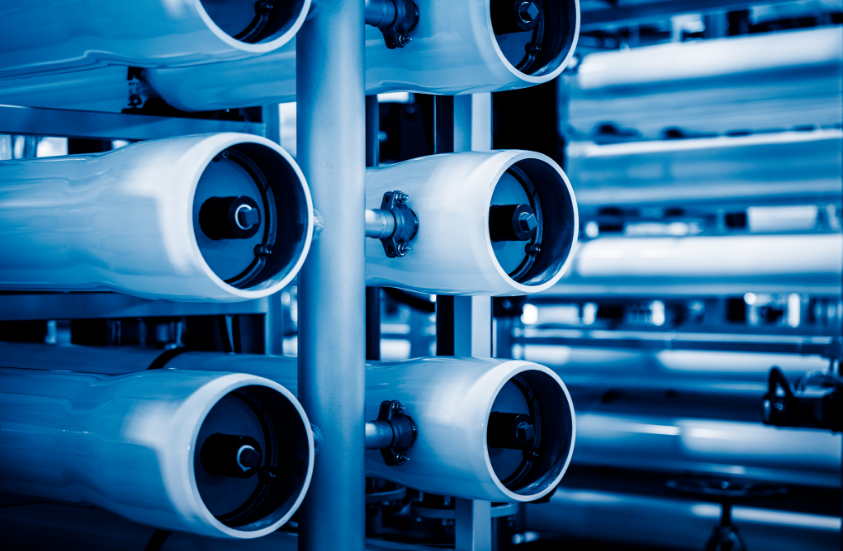
TYPES OF SEAWATER DESALINATION TECHNOLOGIES
There are two main types of seawater desalination technologies: membrane-based (RO) and thermal (MED, MVC). Reverse Osmosis (RO) desalination uses the principle of osmosis to remove salt and other impurities by transferring water through a series of semi-permeable membranes. Thermal desalination uses heat, from power plants or refineries, to evaporate and condense water to purify it.
Each project and customer has its unique requirements and challenges that IDE strives to meet. A variety of factors come into play when selecting the appropriate solution for each project, the required capacity, quality of the source water, quality of the water produced, and energy requirements.


IDE - A DESALINATION WORLD LEADER
IDE leads the water industry with some of the world’s most advanced thermal and membrane desalination plants. We have provided small to large cost-effective desalination solutions in over 500 plants in 50 countries for more than 6 decades. IDE works in partnership with a wide range of customers: municipalities, energy, mining, and power plants, on all aspects of water projects and delivers approximately 3 million m3/day of high-quality water worldwide.
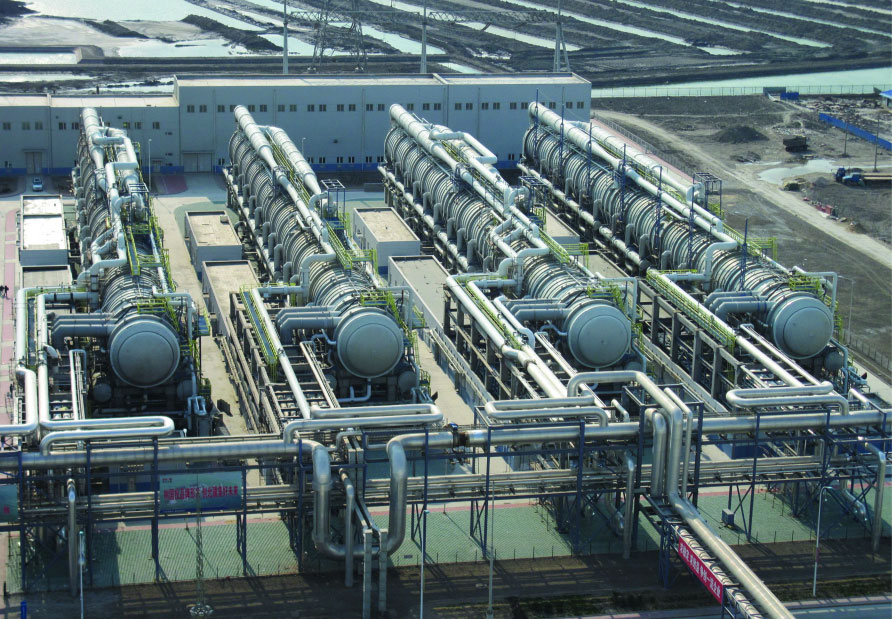



WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF SEAWATER DESALINATION?
Seawater desalination offers several benefits, making it a valuable solution to address water scarcity and ensure a reliable source of freshwater around the world:
– Additional Water Sources: Seawater desalination provides a sustainable and reliable source of freshwater, reducing dependence on rainfall surface water and groundwater, which are limited.
– Improved Water Quality: Seawater desalination produces high-quality freshwater that meets stringent drinking water standards.
– Environmental Conservation: By reducing the need for groundwater extraction or surface water diversion, seawater desalination can help protect natural ecosystems and reduce the ecological impact of water resource utilization.
– Drought Resilience: Seawater desalination provides a drought-resistant source of water, which is crucial for communities and industries.
– Economical growth: Desalinated water is suitable for various uses (municipal, industrial, agricultural, and others), thus supporting economic growth and quality of life.



ACHIEVING SUSTAINABLE SEAWATER DESALINATION
As water desalination plants expand globally, they are required to minimize their environmental impact and maximize their sustainability. Over the years, IDE proved that efficient and cost-effective desalination goes hand in hand with sustainability by implementing a variety of environmentally friendly technologies and design approaches.
IDE ensures that our desalination plants fit our customers’ economic and environmental goals. We are continuously improving energy efficiency so as to minimize both Opex and carbon footprint of the plants . Through continual sustainable thinking and technological advancements, IDE has achieved some of the industry’s lowest energy consumption for desalination plants.
Seawater Desalination methods for any challenge
Learn more
-
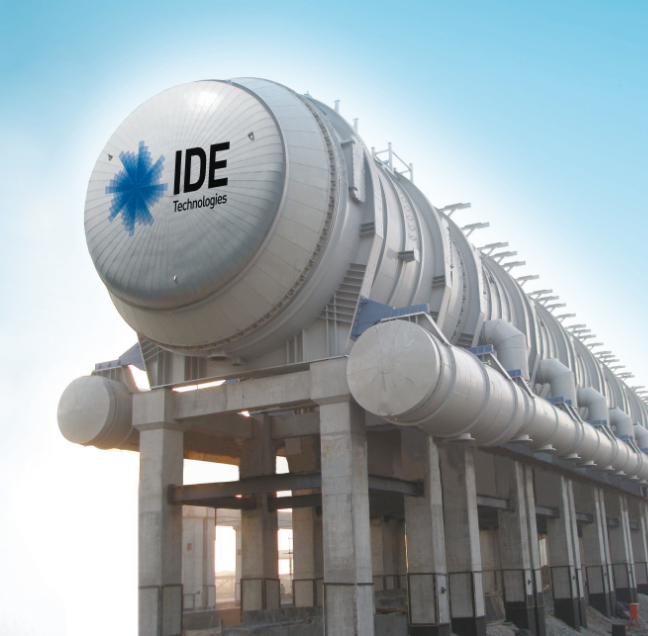

Thermal Solutions
Refineries and power plants generate waste heat. This makes thermal desalination, which uses energy to evaporate water and subsequently condense it again, the most cost-effective solution.
-
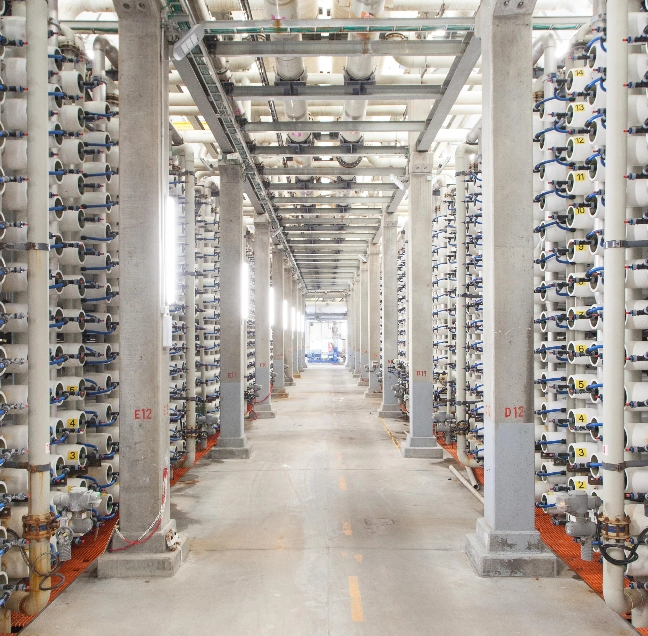

Membrane Solutions
Municipalities, power, oil & gas, mining, resorts and other industries need clean desalinated water for a huge variety of domestic, industrial and agricultural uses.
Our desalination projects
-
Carlsbad Desalination Plant (USA)
Desalination, Reverse Osmosis, SWRO, EP, O&M
Read more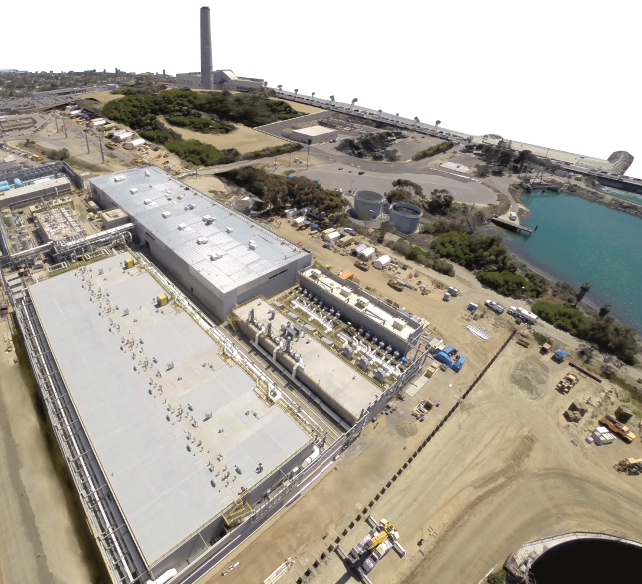
-
Sorek I Desalination Plant (Israel)
Desalination, Reverse Osmosis, BOT, EPC, O&M, P3, Municipal
Read more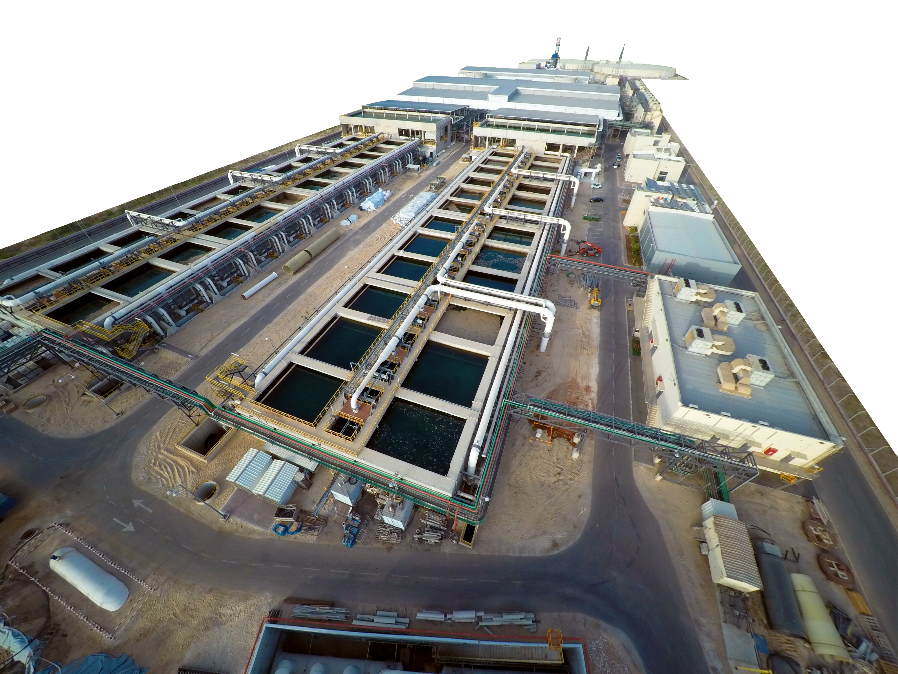
-
Hadera Desalination Plant (Israel)
Desalination, Reverse Osmosis, BOT,EPC, O&M, P3, Financing, Municipal,
Read more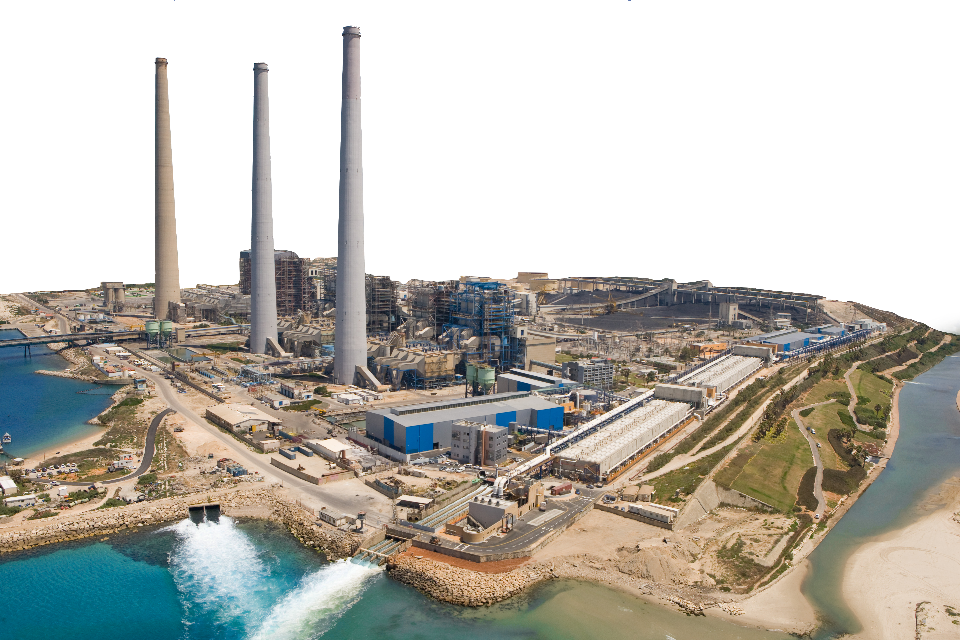
-
Sino Iron Ore Project (Australia)
Desalination, Reverse Osmosis, EPC&S
Read more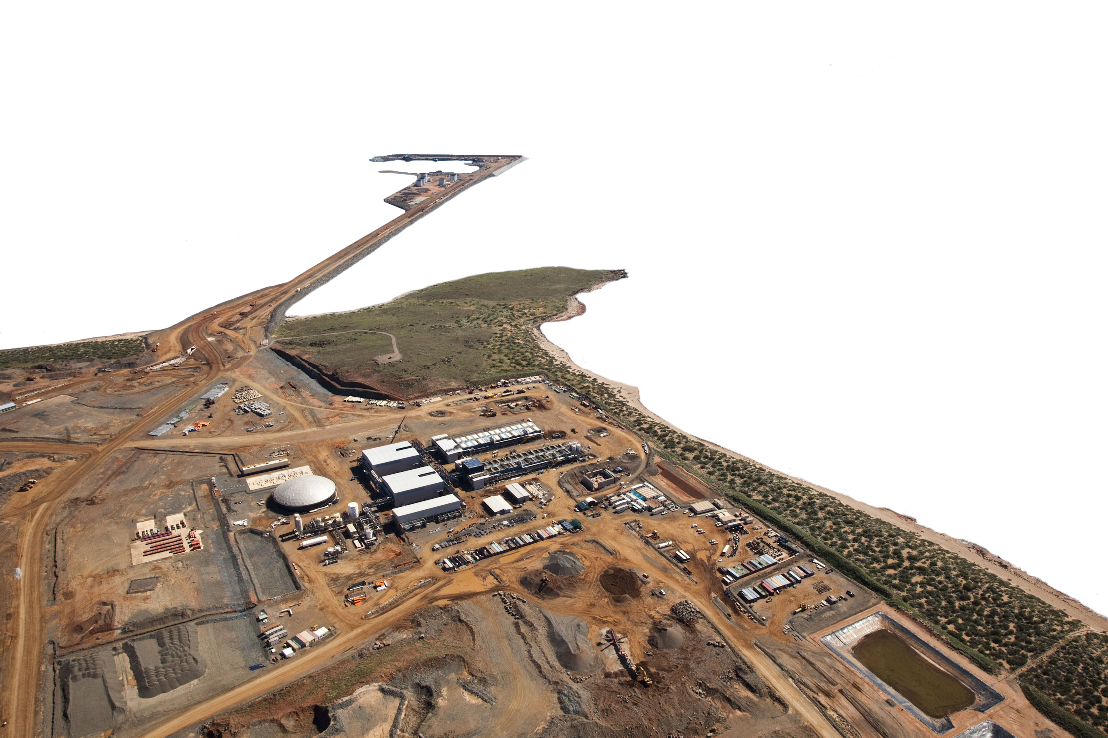

Desalination FAQ
There are approximately 16,000 operational desalination plants, located across 177 countries, which generate an estimated 95 million m3/day of fresh water. Saudi Arabia is the country that relies most on desalination – mostly of seawater. The US is in second place. Per capita SA desalinates more, but the USA desalinates more water overall.
SWRO stands for Seawater Reverse Osmosis, while BWRO stands for Brackish water Reverse Osmosis. S3. Which industries use the most desalinated water?
Desalinated water is a broad term. In general, the power industry and refineries are where it is common to see desalination plants since they are close to the sea and have enough energy to support the desalination process. However, due to new regulations, more and more plants use desalination to reuse their water. They, therefore, provide high-quality water by desalinating treated municipal effluents to industries such as textiles, semiconductors, etc.
Desalinated water is a broad term. In general, the power industry and refineries are where it is common to see desalination plants, since they are close to the sea and have enough energy to support the desalination process. However, due to new regulations, more and more plants use desalination to reuse their water. They therefore, provide high-quality water by desalinating treated municipal effluents to industries such as textile, semiconductors, etc.
The advantage of seawater desalination is that there is no limit to the size of the plant. In addition, proximity to the sea provides an unlimited quantity of feed water and can accept a high amount of concentrated water
A desalination plant is a plant that uses the technology of separating salt from saline water and produces permeate water. This can be done using membrane, distillation, or Ion exchange technology, and more. The most common technology for desalination today is membrane technology.
Contact a desalination expert to learn more about IDE’s desalination plants.
Seawater desalination involves some processes that could impact marine life. However, those impacts can be avoided or minimized by implementing environmental safeguards at every project phase. Therefore, every project needs to have an Environmental Impact Statement.
The cost of desalination can be broken down into the following elements:
- Capital cost (CAPEX) (40 percent)
- Labor (3 percent)
- Membrane replacement (3 percent)
- Maintenance and parts (7 percent)
- Consumables (3 percent)
- Electrical energy (44 percent)
Seawater Desalination has historically been perceived as a more expensive option compared with the traditional treatment of surface or groundwater, . However, one of the latest breakthroughs in desalination has been an improvement in the overall cost, including operational costs (OPEX) and the initial capital expenditure (CAPEX). Very recently, project tenders in Abu Dhabi, Saudi Arabia, and Israel have seen the price fall to the range of $0.50/m3 for the first time.
The average time it takes to design, construct and commission a desalination plant varies by the size, geography and specifics of the plant. For large plants with a capacity of > 100,000 m3/day, 36 to 40 months can be expected. For smaller plants, it’s 15 to 24 months. Again it depends on the complexity of the plant
Wondering how long it took us to build some of our plants? Here are just a few numbers to think about:
- Sorek 1 150 Million cubic m per year -36 months
- Hadera 100 Million cubic m per year 36 months
- Afikey Mayim 6500 cubic m /day 18 months
All desalination technologies have the same byproduct – concentrate or brine. The amount varies depending on the water source being desalinated. Seawater desalination plants discharge more brine – almost 50% of the feed water volume. This is less in brackish water desalination plants -where brine discharged is approximately 15% and 30% of the feed.
Increasing regulatory pressure, growing environmental awareness, and more and larger membrane desalination plants are driving the need for better brine minimization – one of the greatest challenges currently facing the water treatment sector.
The current brine minimization process uses a combination of 3 technologies – reverse osmosis, followed by thermal evaporation, followed by thermal crystallization. There are significant differences in the cost of these technologies.
As with any industrial facility, seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) and brackish water reverse osmosis (BWRO) desalination plants are prone to wear and tear. If not appropriately managed, scaling and fouling are very common issues, leading to membrane clogging and even mechanical failure, affecting the plant’s performance, productivity, and profitability.
IDE’s RO Membrane Management Program (ROMMP) is the best way to keep a constant finger on the plant’s pulse, manage the highest value component of the SWRO system – the RO membranes, and ensure their optimal performance is maintained throughout the operation. Proper operation and maintenance of the RO system are paramount to guaranteeing long-term availability, operational efficiency, and minimal downtime.
IDE plants globally include more than 300,000 installed RO membranes The minimal replacement of membranes in our plants serves as a living testimony to the first-rate maintenance implemented in these plants .
Using the water expertise of IDE Technologies, we identify, develop, design, finance, own, and operate large water infrastructure projects worldwide. With experience dating back to the late 20th century, IDE is a world pioneer in developing PPP projects in the water field. World-class understanding in all disciplines in the water technology market, and unrivalled experience in operation and maintenance of large and complexwater infrastructure projects, allow IDE to optimize the most effective and secured solution to its valued offtakers. A Partnership approach at the forefront of our activities allows efficient risk allocation and the delivery of the most advanced, robust, and most importantly – cost-effective outcome to the of-taker in the shortest possible time.